Enhancing Web Apps with Server-Sent Events
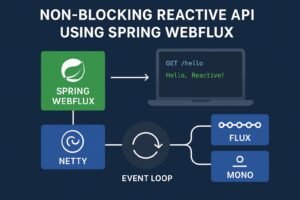
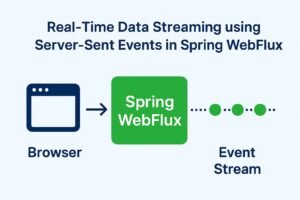
The Age of Real-Time Apps <> While exploring and experimenting with Spring Web Flux, I stumbled upon an interesting feature called Server-Sent Events (SSE) (rather an HTML5 standard) . Although I haven’t had the opportunity to use SSE in my professional projects yet, it immediately caught my attention — both for how it works and the real-time advantages it offers. I was curious to understand where it fits as a component within a modern, real-time application architecture. Here’s a summary of…