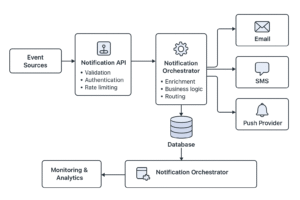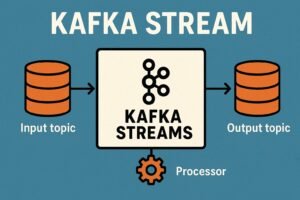
Kafka Streams
From Producers to Real-Time Topologies When you first step into the world of Apache Kafka, it feels like walking into a busy airport. Producers are like airplanes constantly landing with new passengers (data), Consumers are like buses waiting to pick up those passengers, and Kafka Streams is the control tower that orchestrates real-time decisions. In this blog, I’ll walk you through Kafka’s journey — starting from basic Consumers, touching on scalability and offsets, and then moving into the Kafka Streams API,…